Key matrices concepts include identity, determinant, inverse, and singular matrices, which help describe matrix properties and transformations.
Matrices are important tools in mathematics and science. They are used to solve systems of equations, describe transformations, and model real-life problems such as economics, physics, and computer graphics.
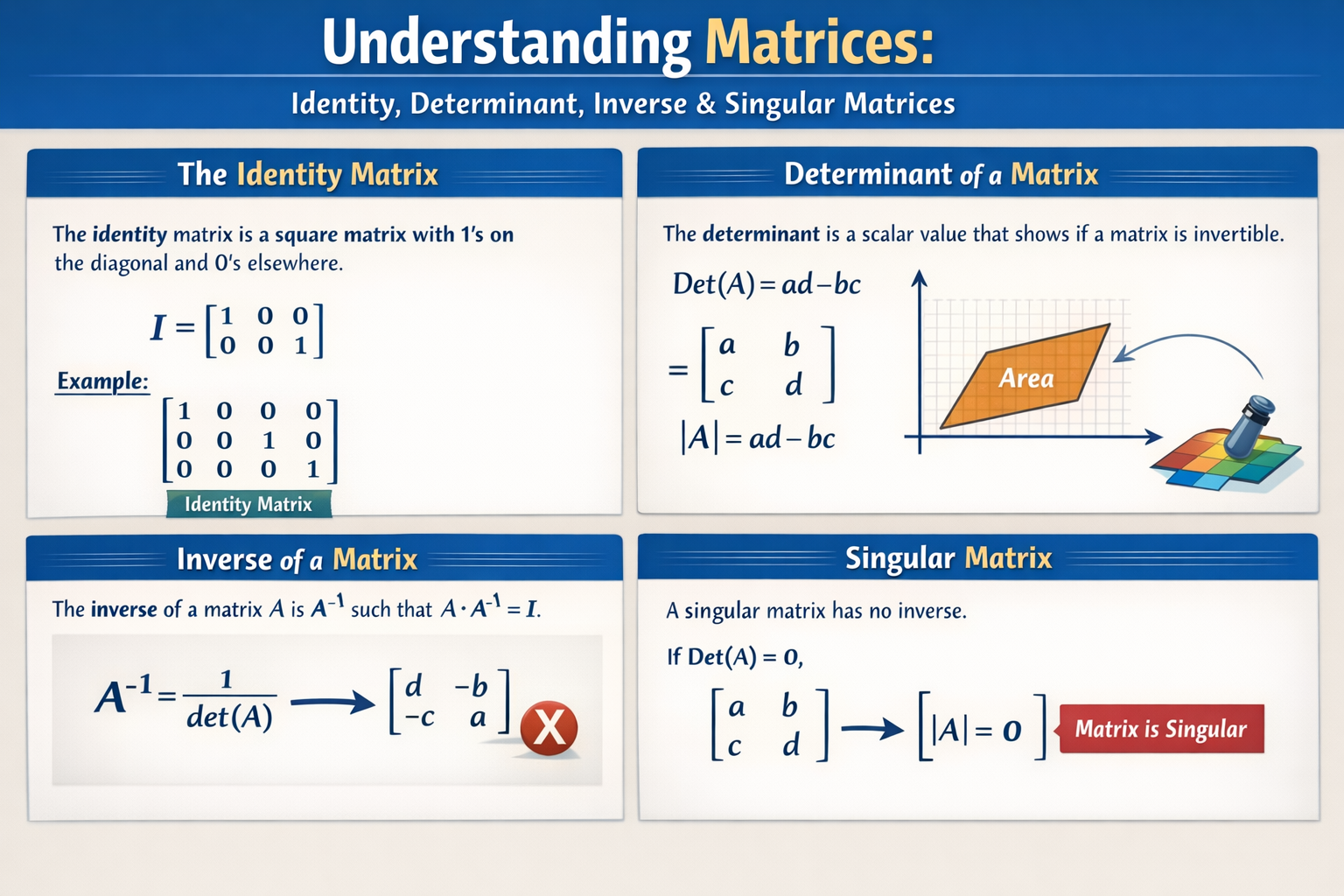
In this lesson, we will learn four important concepts related to square matrices:

- Identity Matrix
- Determinant of a Matrix
- Inverse of a Matrix
- Singular Matrix
2. Identity Matrices
Definition
An identity matrix is a square matrix that has:
- 1’s on the main diagonal
- 0’s everywhere else
It is similar to the number 1 in multiplication, because multiplying any matrix by the identity matrix gives the same matrix.
Notation of matrices
The identity matrix is denoted by I.
2 × 2 Identity Matrix
3 × 3 Identity Matrix
I3=100010001
Illustration
Main diagonal → 1 1 1
Other entries → 0 0 0
Property
3. Determinant of a Matrix
Definition
The determinant of a square matrix is a single number that tells us important information about the matrix, such as:
- Whether the matrix has an inverse
- Whether the system of equations has a unique solution
- The scaling factor of a geometric transformation
Determinant of a 2 × 2 Matrix
For a matrix:
The determinant is:
Example
A=[3124] ∣A∣=(3×4)−(2×1)=12−2=10
The determinant represents area scaling:
- If |A| = 2 → area doubles
- If |A| = 0 → area collapses to a line
4. Inverse of a Matrices
Definition
The inverse of a matrix A is another matrix A−1 such that:
Inverse of a 2 × 2 Matrix
For:
Note: The inverse exists only if the determinant is not zero.
Example
Step 1: Find determinant:
Step 2: Find inverse:
Illustration
Matrix A → changes a vector
Inverse A⁻¹ → returns it back to original
5. Singular Matrix
Definition
A singular matrix is a matrix that has no inverse.
Condition
A matrix is singular if: ∣A∣=0
Example
A=[2142] ∣A∣=(2×2)−(4×1)=4−4=0
Therefore, A is singular and cannot be inverted.
Illustration
Transformation squashes shape into a line → no way to reverse it
6. Summary Table
| Concept | Meaning | Key Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Identity Matrix | Matrix with 1’s on diagonal | Acts like number 1 |
| Determinant | Single number describing matrix properties | The matrix is not a zero matrix |
| Inverse Matrix | Matrix that reverses A | Exists if A exists |
| Singular Matrix | Matrix without inverse |
7. Practice Questions
Question 1
Find the determinant of:
Answer:
Question 2
Write the 3 × 3 identity matrix.
Answer:
Question 3
Determine whether the matrix is singular:
Answer:
Matrix is singular.
Question 4
Find the inverse of:
Answer:
8. Conclusion
Understanding identity, determinant, inverse, and singular matrices is important in solving systems of equations, physics, engineering, and computer science. These concepts help us understand when a matrix can be reversed and how it transforms.

Leave a Reply