- Example 1
- solution
- solution
- Example
- solution
- substitution Problem involving trigonometric ratios
- Example on trigonometric substitution
- Integration by substitution: natural log by substitution
- Example on sec trigonometric ration
- Example 3 on trigonometric ratio
- Practice exercise
- Related Topics
In Calculus, Integration by substitution is when we replace an integral value or its parts in an attempt to make the expression easier to integrate.
Consider the function f(u) such that u is a function of x.
let u = f(x) and f(u)=u
ddxf(u)=dudxf′(u)ddxf(u)=dudxf′(u)
where:
f′(u)=df(u)duf′(u)=df(u)du
Integrating….;
∫dudxf′(u)dx=∫ddxf(u)dx=f(u)+C∫dudxf′(u)dx=∫ddxf(u)dx=f(u)+C
but:
f′(u)=df(u)duf′(u)=df(u)du
so that
∫f′(u)du=f(u)+c∫f′(u)du=f(u)+c
∫dudxf′(u)dx=∫f′(u)du=f(u)+C∫dudxf′(u)dx=∫f′(u)du=f(u)+C
Example 1
Solve the problem below using Integration by substitution:
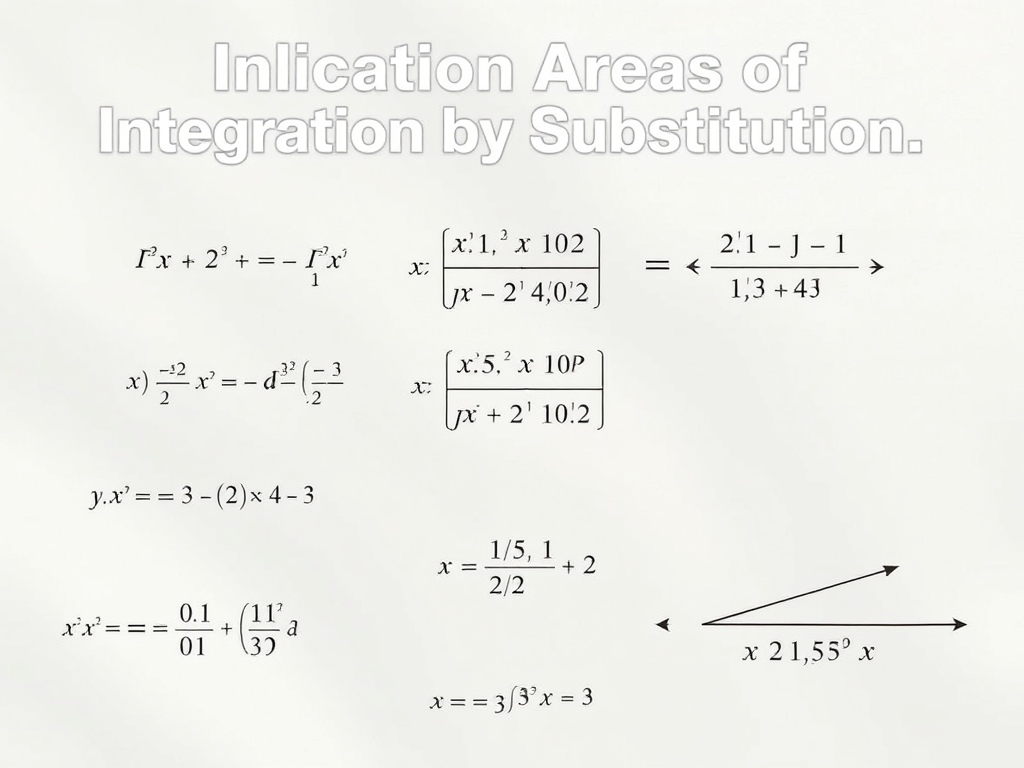
∫x2√x3+5∫x2x3+5
solution
substitute the expression under the root sign as shown:
let
u=x3+5u=x3+5
then integrating u with respect to x we get:
dudx=3x2dudx=3×2
and so:
du=3x2dxdu=3x2dx
and making dx the subject:
dx=du3x2dx=du3x2
rewriting the expression:
∫x2√x3+5=∫x2√udu3x2∫x2x3+5=∫x2udu3x2
x2 on the numerator can then be cancelled out by the x2 on the denominator.
The expression becomes:
∫√Udu3x2=∫u123du∫Udu3x2=∫u123du
=
=13∫U12du=13∫U12du
13.U3232+C=2U329+C13.U3232+C=2U329+C
13.U3232+C=2U329+C=29(x3+5)32+C13.U3232+C=2U329+C=29(x3+5)32+C
Example 2
solve :
∫2x√1+x2dx∫2×1+x2dx
solution
let u = 1 +x2
then differentiating u with respect to x
dudx=2ududx=2u
and then rearranging:
dx=du2xdx=du2x
then rewriting the integral:
∫2x√udu2x=∫√udu∫2xudu2x=∫udu
2x on the denominator has cancelled the 2x on the numerator so that we only have u that is easy to integrate:
∫√udu=∫u−12du=[u3232+C]∫udu=∫u−12du=[u3232+C]
=2u323+C=2(1+x2)323+C=2u323+C=2(1+x2)323+C
Example
solve by substitution:
∫1√2x+1dx∫12x+1dx
solution
let u = 2x + 1
differentiating u with respect to x we obtain;
dudx=2dudx=2
now we express dx in terms of u as:
du=dx2du=dx2
Then we need to rewrite our integral as:
∫1u12du2=12∫u−12du∫1u12du2=12∫u−12du
then:
∫u−12du=12[u1212]+C∫u−12du=12[u1212]+C
=U12+C=U12+C
rem U = 2x + 1
and any number raised to power of 1/2 is like finding it’s squareroot
hence:
U12+C=√2x+1+CU12+C=2x+1+C
substitution Problem involving trigonometric ratios
solve:
∫cosxsin3xdx∫cosxsin3xdx
solution:
let u = sin x: then
dudx=cosxdudx=cosx
dx=ducosxdx=ducosx
and applying substitution in our integral, we replace dx;
∫cosxsin3xdx=∫cosx.u3ducosx∫cosxsin3xdx=∫cosx.u3ducosx
cos x in the numerator cancels the one at the denominator that the expression is reduced to:
∫u3du∫u3du
∫u3du=U44+C∫u3du=U44+C
but u = sin x; therefore:
U44+C=sin4x4+CU44+C=sin4x4+C
generally:
∫cosxsinxxdx=1n+1sinn+1+C∫cosxsinxxdx=1n+1sinn+1+C
Example on trigonometric substitution
solve:
∫sinxcos5xdx∫sinxcos5xdx
solution
let u = cos x
du=−sinxdxdu=−sinxdx
du−sinx=dxdu−sinx=dx
rewriting dx in our original integral:
∫sinxcos5xdx=∫sinxcos5xdu−sinx∫sinxcos5xdx=∫sinxcos5xdu−sinx
we eliminate sin x in the integral to obtain the following expression:
=∫−cos5xdu=∫−cos5xdu
but cos x = u
hence cos5x = u5 and so the integral becomes:
−∫u5du−∫u5du
hence we get:
−∫u5du=−u66+6−∫u5du=−u66+6
and then replacing u for cos x we get:
−cos6x6+C−cos6x6+C
in general:
∫sinxcosnxdx=−1n+1cosn+1x+C∫sinxcosnxdx=−1n+1cosn+1x+C
Integration by substitution: natural log by substitution
solve:
∫lnxxdx∫lnxxdx
solution
let u = lnx
dudx=1xdudx=1x
x du = dx
hence we write the integral as:
∫lnxxdx=∫lnxxxdu∫lnxxdx=∫lnxxxdu
and so we eliminate x to have the integral:
∫lnxdu=∫udu∫lnxdu=∫udu
∫udu=u22+C=(lnx)22+C∫udu=u22+C=(lnx)22+C
Example on sec trigonometric ration
solve:
∫sec2(3x−1)dx∫sec2(3x−1)dx
solution
let u = 3x-1
dudx=3dudx=3
du = 3dx
dx=du3dx=du3
∫sec2udu3=13∫sec2udu=13tanu+c=13tan(3x−1)+C∫sec2udu3=13∫sec2udu=13tanu+c=13tan(3x−1)+C
Example 3 on trigonometric ratio
integrate:
∫sinxecosxdx∫sinxecosxdx
solution
let u = cos x
du=−sinxdxdu=−sinxdx
dx=du−sinxdx=du−sinx
=∫sinxeudu−sinx=−∫eudu=−eu+c=∫sinxeudu−sinx=−∫eudu=−eu+c
Practice exercise
use the substitution method to evaluate the following integrals:
1.∫x(x2−3)4dx∫x(x2−3)4dx
2.∫x√1−x2dx∫x1−x2dx
3.∫cos2x(sin(2x+3))2dx∫cos2x(sin(2x+3))2dx
4.∫ex√1+exdx∫ex1+exdx
5.∫sec2xtan2xdx∫sec2xtan2xdx
6.∫√x√1+x32dx∫x1+x32dx
7.∫(x+1)sin(x2+2x+2)dx∫(x+1)sin(x2+2x+2)dx
8.∫(x+1)√x2+2x+3dx∫(x+1)x2+2x+3dx
9.∫x2(x3+8)4dx∫x2(x3+8)4dx