Exams questions on X-rays often cover topics like the production, properties, and applications of X-rays. They also address their interaction with matter. Common questions ask about the continuous and characteristic spectra produced in an X-ray tube. They inquire about the effects of changing the anode voltage or using filters. Questions also explore the mechanisms behind X-ray production. Other areas include the dual nature of X-rays (wave-particle duality), their relationship to electromagnetic radiation, and their interaction with biological tissues, including both beneficial and harmful effects:
Exam questions on X-rays
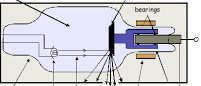
1. Figure 1. Shows part of an x-ray tube

(i) Explain how x-rays are produced in the tube. (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) What property of tungsten makes it suitable for use as a target? (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iii) Why is the anode made of thick copper metal? (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iv) Why is it necessary to have a vacuum inside the tube? (2mks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(v) What effect will increasing current through the filament have on x-ray produced? (1mk)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(vi) What effect will increasing the p.d have on the x-rays produced? (2mks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) The accelerating voltage between cathode and anode is 1000V. Calculate the
(i) Energy possessed by the electrons across the tube. (3mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Speed of the electrons (take e = 1.6 x 10-19 C me = 9.1 x 10-31 kg) (3mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2. (a) Explain why an x-ray tube is evacuated. (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) Distinguish between ‘hard and soft’ x – rays (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
3. X-rays are passed through the air surrounding a charged electroscope.
State what is observed. (1 mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
4. Figure 11 shows the circuit of a modern X-ray tube.

(i) Indicate the path of the X-ray beam supplied by the tube. (1 mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Name the part labeled C and state its function. (2 mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii) Name a suitable metal that can be used for the part labeled B and
give a reason for your choice. (2 mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iv) How can the intensity of x-rays in the tube be increased. (1 mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Exam questions on X-rays
4. The diagram in figure 10 below shows an X-ray tube

(i) What is the nature of the voltage across AB? (1 mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii)Give the name of this X-ray tube (1 mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii) How can the intensity of the X-rays be reduced (1 mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iv) The potential difference between the anode and the cathode is 40KV. what would be the maximum velocity of the electron hitting the target? Take the mass of an electron to be 9.1 x 10-31kg and the charge of an electron as 1.6 x 10-19C (3 mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(v) State what happens to thee quality of the X-rays if this voltage is increased (1 mk)
Related Topics
- Albert Einstein
- Electromagnetic waves
- Examination questions on current electricity
- Exam Questions on density